- Shapes
- Rectangle
- Square
- Circle
- Triangle
- Rhombus
- Squircle
- Oval
- Hexagon
- Pentagon
- Trapezoid
- Kite
- Parallelogram
- Quadrilateral
- Polygon
- Nonagon
- Heptagon
- Decagon
- Octagon
- Ellipse
- Parallelepiped
- Tetrahedron
- Cylinder
- Prism
- Sphere
- Pyramid
- Frustum
- Polyhedron
- Dodecagon
- Dodecahedron
- Octahedron
- Torus
- Cube
- Cone
- Hyperbola
- Rectangular Prism
- Fibonacci Sequence
- Golden Ratio
- Parabola
- Worksheets
- Calculators
- Angle
- Arithmetic
- Whole Numbers
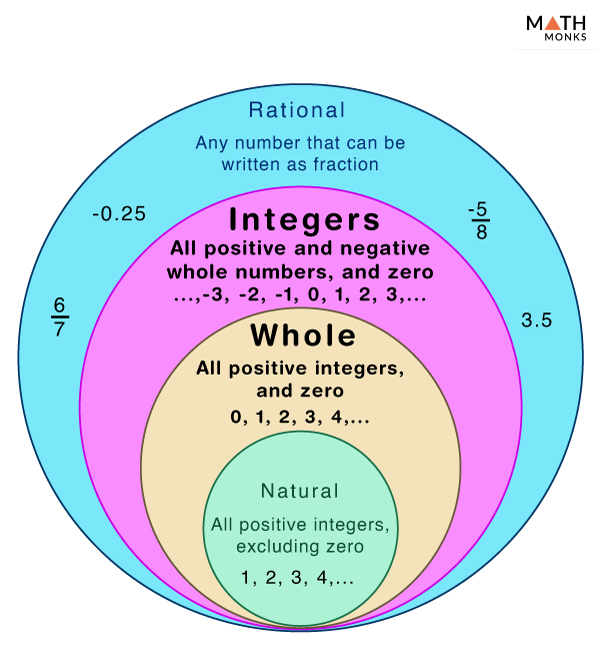
- Rational Numbers
- Place Value
- Irrational Numbers
- Natural Numbers
- Binary Operation
- Numerator and Denominator
- Decimal
- Order of Operations (PEMDAS)
- Scientific Notation
- Symmetry
- Fractions
- Triangular Number
- Complex Number
- Binary Number System
- Logarithm
- Binomial Theorem
- Quartic Function
- Mathematical Induction
- Group Theory
- Modular Arithmetic
- Euler’s Number
- Inequalities
- Sets
- De Morgan’s Laws
- Transcendental Numbers
- About Us
Search