- Shapes
- Rectangle
- Square
- Circle
- Triangle
- Rhombus
- Squircle
- Oval
- Hexagon
- Pentagon
- Trapezoid
- Kite
- Parallelogram
- Quadrilateral
- Polygon
- Nonagon
- Heptagon
- Decagon
- Octagon
- Ellipse
- Parallelepiped
- Tetrahedron
- Cylinder
- Prism
- Sphere
- Pyramid
- Frustum
- Polyhedron
- Dodecagon
- Dodecahedron
- Octahedron
- Torus
- Cube
- Cone
- Hyperbola
- Rectangular Prism
- Fibonacci Sequence
- Golden Ratio
- Parabola
- Worksheets
- Calculators
- Angle
- Arithmetic
- Whole Numbers
- Rational Numbers
- Place Value
- Irrational Numbers
- Natural Numbers
- Binary Operation
- Numerator and Denominator
- Decimal
- Order of Operations (PEMDAS)
- Scientific Notation
- Symmetry
- Fractions
- Triangular Number
- Complex Number
- Binary Number System
- Logarithm
- Binomial Theorem
- Quartic Function
- Mathematical Induction
- Group Theory
- Modular Arithmetic
- Euler’s Number
- Inequalities
- Sets
- De Morgan’s Laws
- Transcendental Numbers
- About Us
Search
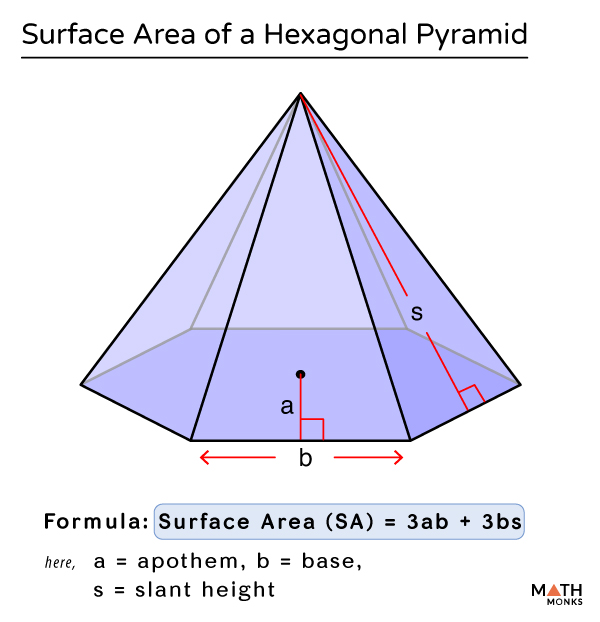
When exactly does the alternative formula work?
It works as the basic formula cannot be applied here.
We use the alternative formula to calculate the surface area of a hexagonal pyramid when the base and height are known.